This is interesting. Russia is delving into the PMSC game and looking to use Cossacks as a stepping stone for that.
I was also interested to see where the talent pool for these Cossack PMSC’s would come from? Well one clue that I came across was the forming of a Cossack party in Murmansk Oblast. This particular group was formed in the military town of Aleksandrovsk and these guys will supposedly be used for the following duties.
Among the assignments of the regional Cossack movement will be to guard the border to Norway and Finland, as well as to engage in fire fighting, street patrolling, and give military-patriotic teaching of children and young people, local Cossack representatives said.
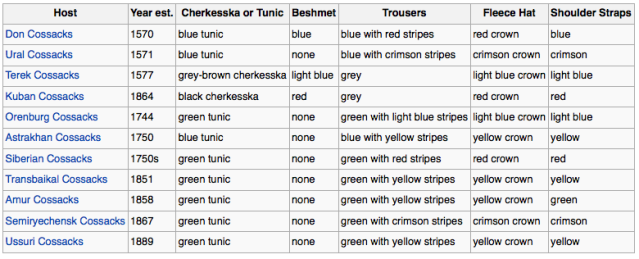
It should be noted that there are Cossack groups all over Russia, so it’s hard to say where these companies would come from. Here is a break down of those various groups (wikipedia). You could probably use the color code below to determine where Cossack PMSC’s came from for future reference.
If anyone has anything to add to this information, I am all ears. The Russian PMSC market is something that is of interest to me, but I just do not have the resources or speak the language to really make any accurate assessments about that market. I am also weary of using Russian media sources for this stuff, but that is all I have. So feedback on this would be great. –Matt

Cossack security firms to guard Russian state property
18 October, 2012
By Ramil Sitdikov
Russia will use Cossack security troops to guard military industrial objects both on its territory and abroad, says the head of the Presidential Council for Cossack issues.
The registration of the special Cossack security firms has already started, Aleksandr Beglov told reporters. Special Cossack troops can be used for providing security only to government and state-owned enterprises at federal and municipal levels, but not to private companies, added the official, who also holds the post of presidential plenipotentiary to the Central Federal District.
The Defense Ministryhas already agreed to sign contracts with Cossack companies so that they guarded some of the facilities that are now guarded by “paramilitary security structures,” Aleksandr Beglov noted.
Russia’s defense industry chief, Dmitry Rogozin, has reportedly supported the idea and said that Cossacks should provide security at various foreign-based facilities as foreign companies charge too much for such work.
Beglov added that Cossacks were planning to found and register their own Cossack Party. The founding convention is scheduled for November 24 and the leader of the new party will be elected at the same time, he said.
The official also told reporters that there were plans to set up several new associations of public organizations that would deal with problems of ethnic Russians residing abroad.
Acording to Beglov, President Putin has recently signed the strategy of the development of the Cossack movement until 2020. The document defined the ways of cooperation between Cossack organizations and state authorities of all levels. The financing of the Cossack movement will be regulated by separate programs, Beglov added.
Cossacks were a separate social group in Tsarist Russia, providing servicemen to the army and guarding the country’s borders in exchange to personal freedoms and preferences. Cossacks were monarchists and extreme nationalists, many of them were subject to repressions after the Bolshevik revolution.
Since the breakup of the Soviet Union, the Cossack movement has slowly been reviving, but it is still split and lacks state support as the government only recently started paying attention to it.
The situation is slightly different in the south of the country, especially in the Krasnodar Region – one of the territories in which Cossacks have traditionally lived. The regional governor has cooperated with Cossack troops for a long time and recently ordered that Cossacks patrolled public territory and provided security at public events.
The move drew criticism from human rights activists over fears of Cossack xenophobia, but so far no real conflicts have arisen.
Story here.
—————————————————————-
War to become a private affair
October 17, 2012
Nadezhda Sokolova
Dmitry Rogozin’s recent statement that Russia’s military-industrial commission is examining the creation of a private military sector is a sign that the market of private military services may soon come out of the shadows.
In the future, Russia’s private military companies (PMCs) could become independent domestic players, free to side with any of the “centers of power” in existence at the time.