Iraq has ambitious plans to develop its huge southern oilfields – potentially the world’s biggest source of new oil over the next few years – and few oil firms dare risk being barred from such a bonanza by angering Baghdad.
But increasingly, some executives say, Kurdistan’s potential is also coming up in boardroom discussions, as sluggish output, red tape and infrastructure bottlenecks in the south take some of the shine off the central government’s oil program.
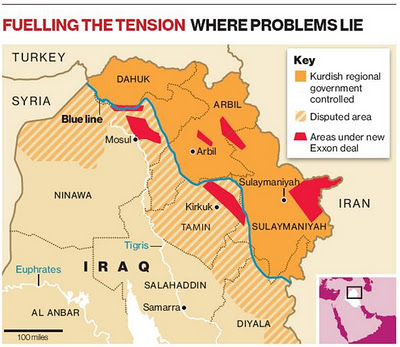
Oil majors are now waiting on the sidelines, watching the outcome of Exxon’s balancing act between Baghdad and Arbil, the northern capital. France’s Total is the latest company to provoke Baghdad’s ire by acknowledging interest in Kurdistan.
“What companies are trying to do is get to the point where they are investing in the north and the south,” said one industry source working in Iraq……Firms have experienced problems getting visas for contractors and security staff, delays in bringing in armored vehicles and holdups securing operating licenses. Such hassles make Kurdistan’s offerings look more tempting by comparison.
“Every delay we face cuts off a significant part of the internal rate of return,” said one oil company source. “Sometimes I wonder if we picked the wrong region.”
This is some interesting business going on in Iraq. Oil companies are playing a risky game in Iraq, and yet they are the actors that will more than likely drive Iraq to ‘pull it together’. It also looks like Exxon Mobil is leading the charge in this game as well.
I say this, because the divisions in Iraqi parliament/central government, along with corruption, is causing oil companies to seek safer and more stable leadership/relationships to do business with in order to keep extracting and shipping oil. For example, Exxon has signed contracts both in the North and the South, and it looks like they are starting to lean more towards moving north with the hopes that this will send a message to parliament. Of course parliament reacted by saying they cannot bid on any more contracts in the south.
The other area of interest with this, are the contracts signed in the disputed areas. Specifically the area near Mosul, which is the second largest city in Iraq. I could see Exxon having all sorts of problems in that region unless some serious deals were made, and I was curious as to what the motivation was? Perhaps the clues are in the state of affairs within the city itself. Check this quote from an interview with Mosul’s governor?
Mosul is an agricultural and oil region. However, it cannot properly and sufficiently use Iraq’s oil revenues. Mosul is also uncomfortable with the recent agreements between foreign oil companies and Arbil to extract oil from Mosul’s soil. For instance, Exxon-Mobil signed a contract with the KRG despite the fact that the site it will explore for oil is in Mosul. Nujaifi is holding talks with Exxon-Mobil and the KRG to resolve this problem. In addition, under the Iraqi constitution, Mosul should get 11 percent of Iraq’s oil revenue. However, it receives only 2 percent. According to Nujaifi, if the oil bill is not adopted and the oil revenues are not distributed evenly by the provinces, a political crisis will erupt. The poverty rate in Mosul is 23 percent, whereas it is 3 percent in the KRG. Nujaifi notes that the rising tension along the borders of Mosul is creating tension for them as well. As the KRG becomes more popular, it is impossible to explain the recent state of backwardness in Mosul.
I highlighted the key parts in this quote, and I think that is most significant. With poverty as high as it is, and a neighbor like KRG enjoying the good life, who do you think Mosul will want to do business with? Especially if Iraq is only giving Mosul 2 % of Iraq’s oil revenue. They are definitely getting the short end stick in this deal, and either the South pays up, or Mosul will probably join the Exxon party.
Also, the news of Kurdistan signing a deal with Turkey for a new pipeline that would completely shut out Baghdad is definitely some news to talk about here. That would mean they would have a way to capitalize on oil extraction without paying Baghdad. They could possibly bring cities like Mosul into the mix with this pipeline, and especially if Mosul can capture a better deal.
On Sunday, Iraqi Kurdistan unveiled an agreement to sell oil through Turkey into the international markets, thereby leaving Baghdad completely out of the loop. The Kurdish oil minister Ashti Hawrami said Iraqi Kurdistan will construct a huge 1 million barrel per day pipeline over the next 12 months through which oil and gas will be carried through Turkey.
“We envisage the building of a new pipeline taking Kurdistan’s oil, particularly the heavier component part to Cihan,” Hawrami said at a conference with Taner Yildez, the Turkish energy minister.
Baghdad believes such an arrangement contravenes Iraqi laws, while Kurds assert they can sign any contract regarding their natural resources according to the terms of the constitution.
Oil fields like this also provide jobs to the locals and infuse money into the local economy. Security will be crucial–which means local security companies will be a huge player in this. (although if you look at how MEND operates in Nigeria, you could see the same thing happening in Mosul with insurgents) The question here is would Baghdad send the troops to protect these oil fields? lol Probably not, unless they are included in the oil deal. That is where this get’s interesting, and I am sure criminal groups and insurgents are looking at how they could use this to their advantage.
The other thing to look at is if Exxon and other oil companies have another pipeline they can use, that is being managed by a government that knows what it is doing and is stable, then I could totally see how this would be a better bet for those companies. This is also another signal to Baghdad that ‘hey guys, if you come together and square away your house, then you too can enjoy the same prosperity as the Kurds’.
Or, the Iraqi government can try to exert influence or pull some military moves up north, but good luck there. lol The Peshmerga and terrain will dictate otherwise.
So we will see how it goes. My guess is that Exxon and others will continue to play the North against South in order to keep extracting. They will keep these two players of the country competing for these companies and their capability. That back and forth interaction, might be the kind of business that will force the country to square itself away in order to finally realize their oil extraction goals. The alternative is to be driven apart.
There is a lot of money in the ground, and if Iraq wants it, it will have to do business with the companies that know how to get it out and into the market. That takes compromise and leadership, and a divided parliament and corrupt government in the south will only force companies to take the path of least resistance. –Matt
Analysis: In Iraq, oil majors play north versus south
By Patrick Markey and Peg Mackey
Thu Apr 5, 2012
In the weeks before Iraqi Kurdistan revealed that Exxon Mobil had signed up to explore for oil there, executives at rival Shell faced a dilemma over whether or not to join the U.S. oil major in its foray north and risk angering Baghdad.
The fields in the autonomous region offered rich potential, an easier working environment, better security and attractive contracts. That seemed a winning combination for smaller oil companies already working there, such as Norway’s DNO, even though they struggled to collect profits.
But at the 11th hour, industry sources say, Royal Dutch Shell backed out and decided to focus on a $17 billion gas deal in the south rather than sign exploration contracts with the Kurdish Regional Government, which the central government could dismiss as illegal and could prompt reprisals.
Shell’s caution, Exxon’s silence on its deals and this week’s renewed dispute between Baghdad and Kurdistan over export payments reveal how delicate is the balance companies must manage between a central government and a Kurdish authority locked in a struggle over who controls Iraq’s vast oil wealth.
The dispute over oil is at the heart of a wider disagreement between Iraq’s central government in Baghdad and the Kurdish region, which are also increasingly at odds over regional autonomy, land and political influence.
Iraq has ambitious plans to develop its huge southern oilfields – potentially the world’s biggest source of new oil over the next few years – and few oil firms dare risk being barred from such a bonanza by angering Baghdad.